Polygonal modeling is typically used for hard-edged surfaces that don't bend or in situations where low polygon counts are important, such as modeling for games. With Maya 5, you can easily convert between polygons, SubDs, and NURBS patches. This allows you to begin the model in one format and then convert to another, if necessary, or to use the advantages of editing or rendering a model in another format.
Polygonal Primitives
There are several ways to use primitives to build objects quickly and easily. Use primitives as a starting point, then uses a combination of polygon creation and editing operations to complete a task. The most basic object type is primitive. Primitives are pure shapes that can be used as the basis of creating more complex models. There are six polygonal primitives objects---sphere, Cone, Cylinder, Cube, Plane and Torus.
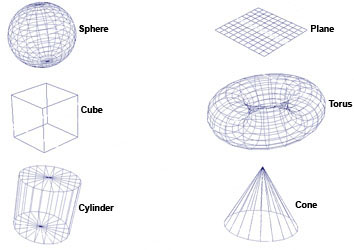
Fig4-1 Polygon primitives
To create a primitive with the default option settings, select create > Polygon Primitives and choose the primitive you want to create from the menu. You can always edit the primitive from the channel Box or its Attribute Editor.
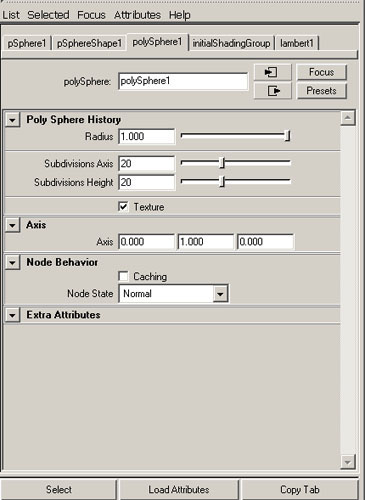
Fig 4_2 Attribute Editor
Section Radius option
The section Radius option value specifies the size of the sections .Change this value to increase or decrease the radius of sections to see the result.
Subdivision Axis
For spheres, cylinders, cones and toruses , this option defines the number of subdivisions there are around the axis defined by the Axis option. This option is also called Subdivisions Axis .Increase or decrease this value to add or take away faces around the axis defined by the Axis option.
Subdivision Height
This option defines the number of subdivisions there are along the axis defined by the Axis option. Height is equivalent to the Y directions by default.Increase or decrease this value to add or take away faces in the Axis direction.
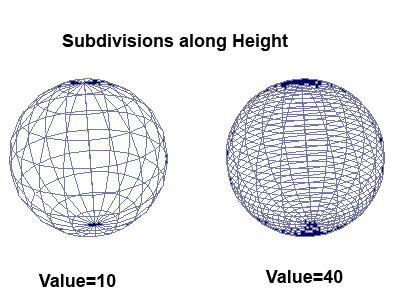
Fig4-3 Subdivision height
Creating and Editing Text
The Poly text type creates text as Polygons .When this text type is selected, a planar trim curve is created between the curves and tessellate nodes. By default, Maya creates text as Nurbs geometry.
To create polygonal text
- Select Create > Text to open the Text Curves option window and set the Type option to poly.
- Type the text you want to write in the text box.
- Change the default font settings if required.
- Change the option settings.
- Click the create button to create the text.
-
Polygonal Text Settings
When you create polygonal text, Maya provides option that you can set to display and create your text for subsequent polygonal-type editing.
Triangles
Three sided polygons are created. This is the default.
Tessellation Methods
Standard fit
This is the default tessellation method. It is adaptive tessellation, meaning that following option is used to determine when to stop the tessellation. The tessellation stops at the fractional tolerance value you set. If there is an edge shorter than the Minimal Edge Length, the tessellation stops on that edge. If the surface is flat enough with in the edge, the tessellation stops here.
General
Set the tessellation method to General to display the following options. Unless Use chord height or use chord height ratio is turned on, a uniform tessellation is performed. Each span is split into a number of polygons depending on the number U and V values you set.
Count
Set the tessellation method to Count to display the Following slider. Count slider is used to determine how many polygons the surface can be tessellated into.
Control points
This tessellation method converts the Nurbs model to polygons while matching the CVs of the original Nurbs surface. There are no other options for this operation.
Extruding
You can pull faces and edges out from polygonal objects using the Extrude Face and Extrude Edge commands.
Extruding Faces
You can extrude faces either interactively or directly through the option window. Select Edit Polygons > Extrude Face ,set whatever option you need and click the Extrude Face button.
- If you want to extrude all the faces of an object, marquee-select the whole object to highlight the faces.
- If you want to extrude certain areas of an object, shift-or Ctrl-click to select those face only.
- If you want to extrude ,duplicate or extract multiple faces together, turn on polygons > Tool options >Keep Faces Together.
you are not happy with results, select Undo from the Edit menu, change the Extrusions settings in the channel Box or Attribute Editor and press Enter.
Extruding Edges
You can extrude edges either interactively or directly through the option window. If you prefer to set the options first and then extrude the edges, Select Edit Polygons > Extrude Face.
Duplicating Faces
You can duplicate and transform faces interactively or directly through the option window. Select the faces of the object you want to duplicate. Press the right mouse button and select Face or press F11.
- If you want to duplicate all the faces of an object, marquee-select the whole object to highlight the faces.
- If you want to duplicate certain areas of an object, click to select those face only.
You can also Duplicate Faces through Edit Polygons > Duplicate Face.
Extracting Faces
While Extracting ,Maya disconnects the selected Faces from the original shape, by duplicating the appropriate edges and vertices. The extracted faces become their own shell with in the object. This is the another way to make holes in the object while retaining their original faces.
Seperating the extracted faces creates distinct polygons out of the faces and the original object.
To extract Faces
- Select the face of the object you want to extract. Press the right mouse button and select Face from the marking menu or press F11,then shift or Ctrl-Click to select the faces.
- Select edit Polygons > Extract. The selected Faces are extracted.
Fig4-4 Extracting faces
Smoothing Polygons
There are three ways to smooth polygons.
- Using Polygons > smooth.
- Using Polygons >Average vertices.
- Using the smooth operation of the sculpt polygons Tool to average the values of painted vertices to produce a smoother surface.
Polygon Selection
With Edit Polygons > Selection menu, you can constrain the selection of components to a specified area of a polygonal model and perform operations on those components in that specified area only without disturbing the rest of the model.
Select Edit Polygon > Selection >Grow Selection Region to increase the number of components you initially selected.
Selecting Boundaries
You use Edit Polygons >Selection >Select Selection Boundary to define the boundary of the current selection region. It is a quick way to select the boundaries of whatever is currently selected.
Selection a band of edges
Use Edit Polygons > Selection > Select Contiguous Edges to select a contiguous band of edges around model. With this you can select one edge, choose select Contiguous Edges, and it will select the rest of the edges in the center automatically.

0 comments:
Post a Comment